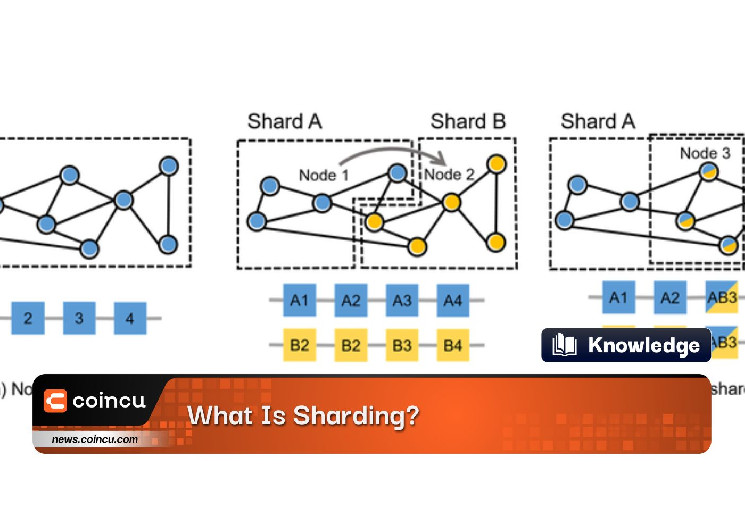
What Is Sharding?
Sharding is a way utilized in distributed database techniques to enhance efficiency, scalability, and availability. It entails dividing a big database into smaller, extra manageable components known as shards. Every shard accommodates a subset of the info, and collectively, the shards kind a whole database.
In a shared database, information is distributed throughout a number of servers or nodes. Every shard is answerable for storing and processing a portion of the info, and no single node accommodates all the dataset. This enables for parallel processing and elevated storage capability, enabling the system to deal with bigger quantities of information and better transaction charges.
The division of information into shards is usually based mostly on a selected shard key, which could be a particular attribute or a variety of values. The shard key determines how the info is partitioned throughout the shards. By rigorously deciding on the shard key, the system can evenly distribute the info and steadiness the workload throughout the nodes.
Sharding gives a number of benefits:
- Scalability: As the quantity of information grows, further shards could be added to the system, permitting it to deal with elevated workloads and assist extra customers with out sacrificing efficiency.
- Efficiency: Sharding allows parallel processing by distributing information throughout a number of nodes. This can lead to sooner question response occasions and improved total system efficiency.
- Availability: For the reason that information is distributed throughout a number of nodes, the failure of 1 node doesn’t end result within the full unavailability of the system. The remaining nodes can proceed to serve requests and preserve information availability.
Nonetheless, sharding additionally introduces some challenges. Complicated queries that require information from a number of shards could be harder to execute, and sustaining information consistency throughout shards could be difficult. Moreover, sharding requires cautious planning and administration to make sure correct distribution of information and cargo balancing.
Sharding is a strong method for scaling and enhancing the efficiency of distributed database techniques, making them able to dealing with massive volumes of information and excessive workloads.
Understanding Sharding
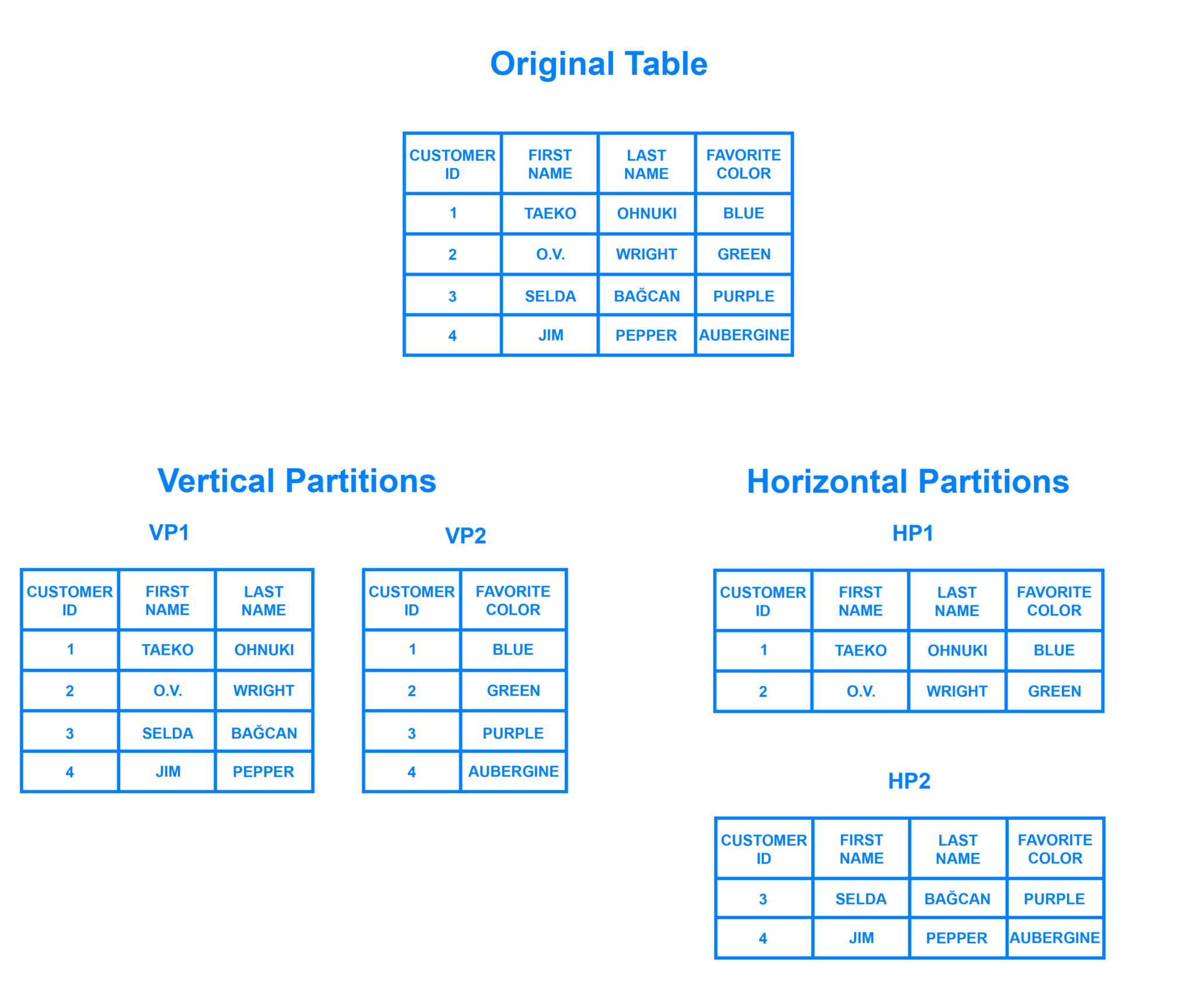
Sharding is a way utilized in database techniques to horizontally partition information throughout a number of servers or nodes. It entails breaking down a big database into smaller, extra manageable items known as shards. Every shard accommodates a subset of the info, and collectively, the shards kind a whole database.
The first purpose of sharding is to enhance the efficiency and scalability of a database system. By distributing information throughout a number of shards, the workload could be unfold out, permitting for parallel processing and rising the system’s capability to deal with bigger volumes of information and better transaction charges.
Listed below are some key facets to grasp about sharding:
- Knowledge Distribution: Sharding entails dividing information based mostly on a shard key. The shard key could be a particular attribute or a variety of values. It determines how the info is partitioned throughout the shards. For instance, in a social media software, the shard key may very well be the consumer ID, guaranteeing that each one information associated to a specific consumer is saved in the identical shard.
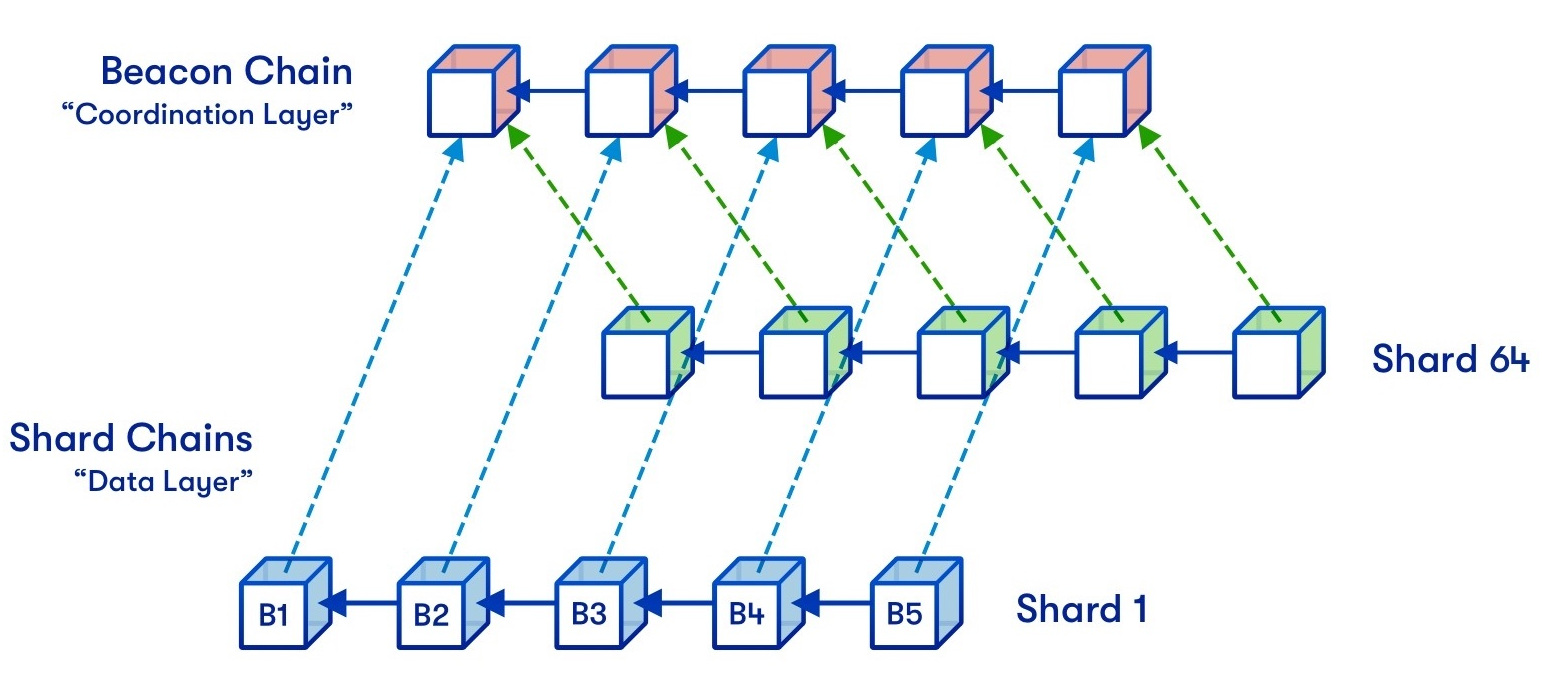
- Shard Independence: Every shard operates independently and could be situated on a separate server or node. This enables for parallel execution of queries and transactions on totally different shards concurrently. It additionally gives fault isolation, so if one shard fails, the opposite shards can proceed functioning.
- Question Routing: When a question is made to the database, a sharding middleware or coordinator determines which shard(s) must be accessed based mostly on the question’s shard key. The middleware then routes the question to the suitable shard(s) for processing. This ensures that queries are directed solely to the related shards, decreasing the quantity of information that must be processed.
- Knowledge Consistency: Sustaining consistency throughout shards could be a problem in sharded databases. Updates that have an effect on a number of shards, often called distributed transactions, require coordination to make sure information integrity. Completely different approaches, comparable to two-phase commit or eventual consistency, can be utilized to handle consistency throughout shards.
- Shard Administration: Sharding requires cautious planning and ongoing administration. The variety of shards, their distribution, and the shard key choice impression the system’s efficiency and scalability. Scaling the system might contain including extra shards, redistributing information, or redefining the shard key.
- Shard Consciousness: Functions that work together with a sharded database must be shard-aware. They have to be designed to route queries accurately, deal with distributed transactions, and handle information locality. Correct software design and improvement practices are essential to leverage the advantages of sharding successfully.
Sharding is usually utilized in large-scale techniques the place conventional approaches to scaling a database, comparable to vertical scaling (including extra sources to a single server), turn into impractical or inadequate. It allows the system to deal with large quantities of information and heavy workloads whereas sustaining efficiency and availability.
How Sharding Is Completed
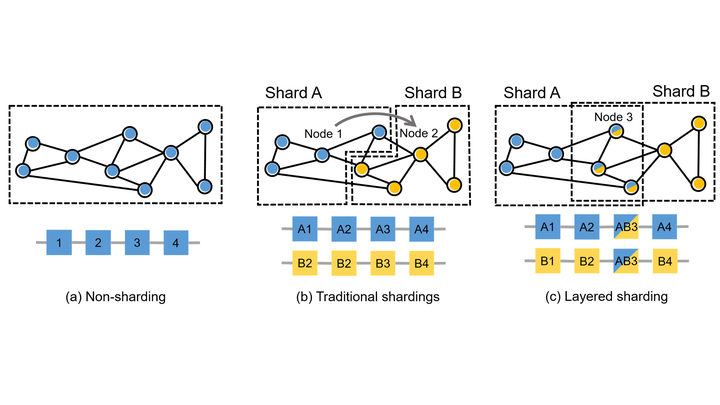
Sharding is completed by means of a mix of information partitioning, question routing, and shard administration methods. Right here’s an outline of how sharding is usually completed:
- Knowledge Partitioning: Step one in sharding is to divide the info into smaller subsets known as shards. There are a number of widespread approaches to information partitioning:a. Vary-based partitioning: Knowledge is split based mostly on a specified vary of values. For instance, if the shard key’s a timestamp, one shard might include information for a particular time interval (e.g., January 1 to January 31), whereas one other shard accommodates information for the subsequent time interval (e.g., February 1 to February 28).b. Hash-based partitioning: Knowledge is distributed throughout shards based mostly on the hash worth of the shard key. The hash operate evenly distributes the info, guaranteeing a roughly equal distribution throughout shards.c. Record-based partitioning: Knowledge is partitioned based mostly on a predefined listing of values. Every shard is assigned a particular worth or set of values for the shard key. For instance, if the shard key’s a rustic code, one shard might include information for the USA, whereas one other shard accommodates information for Canada.
- Question Routing: When a question is made to the database, a sharding middleware or coordinator is answerable for figuring out which shard(s) must be accessed. That is completed based mostly on the question’s shard key. The middleware retains monitor of the shard mappings and routes the question to the suitable shard(s) for processing. The question outcomes from a number of shards could also be mixed or aggregated earlier than being returned to the consumer.
- Shard Administration: Sharding requires ongoing administration to make sure the right distribution of information and cargo balancing. Some widespread duties concerned in shard administration embody:
a. Shard Creation: As the info grows, new shards might must be created to accommodate the elevated workload. This entails allocating new servers or nodes and redistributing the info throughout the present and new shards.
b. Shard Removing: If the info dimension decreases or the workload decreases, it might be essential to take away shards from the system. The information from the shard is redistributed to the remaining shards earlier than the shard is decommissioned.
c. Knowledge Redistribution: Because the variety of shards adjustments, information might must be redistributed to take care of a balanced distribution throughout the shards. This course of entails shifting information between shards whereas minimizing downtime and sustaining information consistency.d. Shard Key Refinement: The selection of a shard key’s essential for environment friendly sharding. Over time, it might be essential to assessment and refine the shard key choice to make sure an excellent distribution of information and optimum question efficiency.
Sharding requires cautious planning and coordination to make sure information consistency, environment friendly question routing, and efficient administration of the shards. You will need to think about elements comparable to information distribution, question patterns, scalability necessities, and system complexity when implementing a sharding technique.
Sharding and Safety
Sharding can have implications for safety in a database system. Listed below are some concerns concerning safety when implementing sharding:
- Knowledge Segmentation: Sharding entails dividing information into smaller subsets or shards. It’s necessary to rigorously think about how information is segmented to make sure that delicate or confidential info is appropriately protected. For instance, you could wish to keep away from inserting extremely delicate information in the identical shard as much less delicate information to reduce the danger of unauthorized entry.
- Entry Management: Sharded databases want sturdy entry management mechanisms to make sure that solely approved customers or purposes can entry particular shards or information. Position-based entry management (RBAC), fine-grained entry management insurance policies, and powerful authentication mechanisms must be carried out to implement entry restrictions and shield delicate information from unauthorized entry.
- Encryption: Encrypting information at relaxation and in transit is important to guard information confidentiality. Sharding shouldn’t compromise the usage of encryption mechanisms. Every shard ought to have encryption carried out to safeguard information throughout the shard. Moreover, when information is transmitted between shards or throughout question routing, applicable encryption protocols (comparable to TLS/SSL) must be used to forestall eavesdropping or tampering.
- Knowledge Integrity: Sustaining information integrity throughout shards is essential. Distributed transactions involving a number of shards ought to be sure that all information adjustments are both dedicated efficiently throughout all related shards or rolled again in case of failure. This ensures that the integrity of the general dataset is maintained and that no unauthorized modifications or inconsistencies are launched.
- Audit and Logging: Sharded databases ought to have complete logging and auditing mechanisms in place. This consists of monitoring and logging all important operations, entry makes an attempt, and modifications made to the info. Centralized logging and monitoring can assist detect any suspicious actions or safety breaches throughout a number of shards.
- Community Safety: Sharded databases sometimes contain a number of servers or nodes speaking with one another. It’s important to safe the community communication between shards, guaranteeing that it’s protected towards unauthorized entry, eavesdropping, or interception. Sturdy community safety measures, comparable to firewalls, VPNs, and safe communication protocols, must be carried out to safe the inter-shard communication.
- Compliance and Rules: Relying on the character of the info being saved, particular trade laws or compliance necessities (comparable to GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS) might must be thought-about. Sharding methods ought to align with these laws to make sure information privateness, safety, and compliance.
- Vulnerability Administration: Common safety assessments, vulnerability scans, and penetration testing must be carried out on the sharded database system to establish and handle any safety vulnerabilities. Immediate patching of software program and firmware vulnerabilities and following safety greatest practices will assist mitigate potential safety dangers.
Conclusion
Sharding is a way utilized in distributed database techniques to enhance efficiency, scalability, and availability. It entails dividing a big database into smaller components known as shards, that are distributed throughout a number of servers or nodes. Every shard accommodates a subset of the info, enabling parallel processing and elevated storage capability.
Sharding gives a number of benefits, together with scalability to deal with bigger information volumes and better workloads, improved efficiency by means of parallel processing, and elevated availability by distributing information throughout a number of nodes. Nonetheless, sharding additionally presents challenges comparable to sustaining information consistency throughout shards and managing advanced queries that contain a number of shards.
Safety concerns are necessary when implementing sharding, together with information segmentation, entry management, encryption, information integrity, and compliance with laws. Correct safety measures, comparable to sturdy entry controls, encryption, audit logging, and vulnerability administration, must be carried out to guard information and guarantee compliance with safety requirements.
General, sharding is a strong method for scaling and enhancing the efficiency of distributed database techniques. It requires cautious planning, efficient administration, and adherence to safety greatest practices to completely leverage its advantages and make sure the safety and integrity of the info.
DISCLAIMER: The Data on this web site is supplied as basic market commentary and doesn’t represent funding recommendation. We encourage you to do your individual analysis earlier than investing.